Basic Points About the Zionist Israeli-Arab Palestinian Conflict
What is the conflict about?
All Global Research articles can be read in 51 languages by activating the Translate Website button below the author’s name (only available in desktop version).
To receive Global Research’s Daily Newsletter (selected articles), click here.
Click the share button above to email/forward this article to your friends and colleagues. Follow us on Instagram and Twitter and subscribe to our Telegram Channel. Feel free to repost and share widely Global Research articles.
Global Research Referral Drive: Our Readers Are Our Lifeline
***
The Zionist Israeli-Arab Palestinian conflict today is one of if not the most significant global security problems to be dealt with.[1] However, this conflict is historically not much old as it is a pretty modern issue, dating, in fact, since the First Zionist Congress in 1897. The focal question is: What is the conflict about? In other words: What are those two different groups fighting for?
At first glance, it can be understood that behind the conflict reasons is a confession as those two peoples are of different denominations: the Jews are predominantly Judaists while the Palestinian predominant confession is Islam but includes Christians and Druze. However, the obvious religious differences are not the fundamental cause of the struggle. In fact, the conflict started a century ago and continued to be strife for the land.
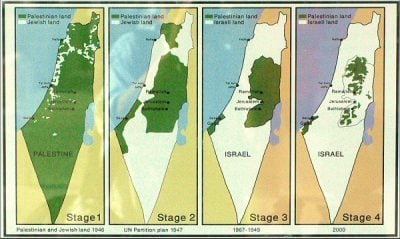
Palestine, the land claimed by both sides was known under this term in international relations (IR) from 1918 till 1948. Moreover, the same term was applied by Islam, Christianity, and Judaism to designate a Holy Land. However, as a consequence of the wars from 1948 to 1967 between the Arabs and Israel, this land (some 10,000 sq. miles) became today divided into three parts: 1) Israel; 2) the West Bank; and the Gaza Strip.
However, both groups have a different background in claiming this land for themself:
- The Zionist Jewish claims to Palestine are founded on the Biblical promise to Abraham and all his descendants. The historical foundations of such claims are based on the fact that on the territory of Palestine have been established the ancient kingdoms of the Jews: Israel and Judea. Politically, this historical claim is backed by the need of the Jews for the nation-state to get rid of European anti-Semitism, especially after the WWII holocaust.
- Arab Palestinians are claiming the same land based on their continuous living in Palestine for hundreds of years and on the fact that they were the demographic majority until 1948. In addition, they reject the confessional-ideological notion of the Zionist Jews that the Jewish kingdoms based on the Old Testament can constitute any rational and moral/scientific foundations to be used for acceptable modern claim especially taking into consideration that the Jews left Palestine after the occupation of the Roman Empire in the 1st century AD (for 2,000 years!). However, the Arab Palestinians also use the arguments from the Bible and, therefore, claim that Abraham’s son Ishmael is the forefather of the Arabs and that God promised the Holy Land to all children of Abraham which simply means to the Arabs too (Arabs are Semitic people as Jews). But the crucial issue from the Arab Palestinian viewpoint is that they cannot forget Palestine as a matter of compensation for the holocaust against the Jews committed in Europe (in which Arab Palestinians did not participate at all).
The Palestinians and Diaspora
The term Palestinians from the very political-historical standpoint today refers to those people of Palestine whose historical roots are traced to this land as defined by the British Mandate’s borders being the Arabs of Christian, Muslim, or Druze denominations.
It is estimated that today some 5.6 million Palestinians are living within the British Mandate Palestine’s frontiers which are now divided into three parts: 1) The State of Zionist Israel; 2) The territory of the West Bank; and 3) the Gaza Strip. The last two were occupied by Israel during The 1967 Six Days War.
It is also claimed that today some 1.5 million Palestinians are living as citizens of Israel. Therefore, the Palestinians compose around 20% of the Israeli population. In addition, some 2.6 million Palestinians live in the West Bank including 200,000 living in East Jerusalem and around 1.6 million living in the Gaza Strip (at least before the current Israeli genocide on the Gazans which started in October 2023). However, there are around 5.6 million Palestinian people who are living in the diaspora, outside Palestine mainly in Lebanon, Syria, and Jordan.
Among all Palestinian diaspora groups, the largest one (some 2.7 million) lives in Jordan (not taking into consideration the territory of the West Bank which legally belonged to the Kingdom of Jordan). Many of them still live in those refugee camps established in 1949 while others became town dwellers. Some Palestinian refugees took refuge in Saudi Arabia or other Arab Gulf states while others moved to other countries of the Middle East or the rest of the world. Among all Arab states, only Jordan granted citizenship to those Palestinians living there. That became, however, the formal reason for some Zionist Jews to claim that Jordan is, in fact, already a national state of the Palestinians and, therefore, there is no real need to establish an independent state of Palestine. On the other hand, nonetheless, many Palestinians claim that the USA is, basically, the national state of the Jews, and, subsequently, Israel in the Middle East does not need to exist (as the second national state of the Jews).
Nevertheless, the situation of the Palestinian refugees in South Lebanon is particularly disastrous as many Lebanese are blaming them for the civil war that ruined the country in 1975−1991 and, therefore, demand that all Lebanese Palestinians have to be resettled somewhere else as a precondition to re-install peace in the country. Especially the Lebanese Christians are very anxious to rid the country of the Muslim Palestinians as they fear that the Palestinians are undermining the religious balance of Lebanon.
Israeli Palestinians
When Israel was proclaimed as an independent state in May 1948, there were only some 150,000 Arab Palestinians within its borders. On one hand, all of them were granted the citizenship of Israel which means automatically and with the right to vote.[2] However, on the other hand, they de facto have been second-class citizens (i.e. the ethnic and confessional minority) for the very reason that Israel was officially defined as both a Jewish state and the state of the Jewish people.[3] The Arab Palestinians are not the Jews (even though both are the Semites).[4] Most of those Israeli Palestinians were subjected before the 1967 Arab-Israeli War to the military authority which restricted their free movement followed by other civic rights like work, free speech, association, etc. The Palestinians were not allowed to be the full members of the Israeli trade union federation (the Histadrut) up to 1965. However, the focal problem was that the State of Israel confiscated around 40% of Palestinian land to be used for development projects.[5] However, from the majority of such state’s development projects, mostly exactly Israeli Jews profited but not Israeli Arab Palestinians.
One of the basic claims by the Arab Palestinians in Israel is that all Israeli authorities are systematically discriminating against them by allocating very few resources for health care, education, public works, economic development, or resources for municipal governmental authorities to the Arab-populated land. Another general claim is that Israeli Palestinians are as well as systematically discriminated against for the right to preserve and develop their cultural, national, and political identity. As a matter of fact, Israeli Palestinians have been up to 1967 totally isolated from the Arab world but as well as very much understood by other Arabs as traitors who left to live in the oppressive Zionist anti-Arab State of Israel. However, since The 1967 Six-Day War, the majority of Israeli Palestinians have become more self-confident in their Arab Palestinian national identity, especially during the last 20+ years as Zionist Israeli authorities prohibited commemorating the Al Nakba which is either the expulsion or flight of at least 500.000 Arab Palestinians in 1948−1949 during the first Arab-Israeli war.
*
Note to readers: Please click the share button above. Follow us on Instagram and Twitter and subscribe to our Telegram Channel. Feel free to repost and share widely Global Research articles.
Dr. Vladislav B. Sotirović is a former university professor in Vilnius, Lithuania. He is a Research Fellow at the Center for Geostrategic Studies. He is a regular contributor to Global Research.
Notes
[1] About the Israeli-Palestinian conflict, see in [Martin Bunton, The Palestinian-Israeli Conflict: A Very Short Introduction, New York: Oxford University Press, 2013].
[2] Nevertheless, in some cases, the Israeli Central Elections Committee in practice used very politically coloured criteria to discriminate against those Arab Palestinians whose political views are understood to be unacceptable, especially at the time of the parliamentary elections.
[3] About the ideological-political background of the creation of Israel as a nation-state of the Jews, see in [Theodor Herzl, The Jewish State: The Historic Essay that Led to the Creation of the State of Israel, Skyhorse, 2019].
[4] Semitic peoples are supposed to descend from Shem, son of Biblical Noah. Particularly it is assumed for the Jews, Arabs, Ancient World’s Phoenicians, and Assyrians [Alan Isaacs, et al (eds.), A Dictionary of World History, Oxford−New York: Oxford University Press, 2000, 563]. There is a claim that, in fact, present-day Palestinians descended from the Phoenicians and that the term Palestinians is corrupted Phoenicians.
[5] Israeli Palestinians are commemorating on March 30th Land Day to protest the continuing confiscation of Arab territories by the Israeli Government. The first protest on this day was in 1976 when the Israeli security forces killed six Palestinians. Since this incident, the Palestinians either in the diaspora or in Israel commemorate this day as a national day.

