National Identities of the People Living in Ukraine. Historical Background

All Global Research articles can be read in 51 languages by activating the Translate Website button below the author’s name.
To receive Global Research’s Daily Newsletter (selected articles), click here.
Click the share button above to email/forward this article to your friends and colleagues. Follow us on Instagram and Twitter and subscribe to our Telegram Channel. Feel free to repost and share widely Global Research articles.
***
Ukraine is an East European territory which was originally forming a western part of the Russian Empire in the mid-17th century. That is a present-day independent state and separate ethnolinguistic nation as a typical example of Benedict Anderson’s theory-model of the “imagined community” – a self-constructed idea of the artificial ethnic and linguistic-cultural identity.
Before 2014 Ukraine was a home of some 46 million inhabitants of whom, according to the official data, there were around 77 percent of those who declared themselves as the Ukrainians.
Nevertheless, many Russians do not consider the Ukrainians or Belarus as “foreign” but rather as the regional branches of the Russian nationality.
It is a matter of fact that, differently to the Russian case, the national identity of Belarus or the Ukrainians was never firmly fixed as it was always in the constant process of changing and evolving [on the Ukrainian self-identity construction, see: Karina V. Korostelina, Constructing the Narratives of Identity and Power: Self-Imagination in a Young Ukrainian Nation, Lanham, Maryland: Lexington Books, 2014].
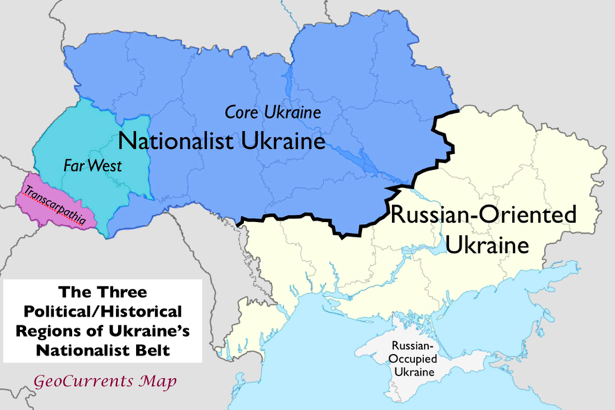
The regions of Ukraine according to the political orientation
The process of self-constructing identity of the Ukrainians after 1991 is basically oriented vis-à-vis Ukraine’s two most powerful neighbors: Poland and Russia. In other words, the self-constructing Ukrainian identity (like the Montenegrin or Belarus) is able so far just to claim that the Ukrainians are not both the Poles or the Russians but what they really are is under great debate. Therefore, the existence of an independent state of Ukraine, nominally a national state of the Ukrainians, is of very doubt indeed from both perspectives: historical and ethnolinguistic.
The Slavonic term Ukraine, for instance, in the Serbo-Croat case Krajina, means in the English language a Borderland – a provincial territory situated on the border between at least two political entities: in this particular historical case, between the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania as the Republic of Both Nations (1569−1795) and the Russian Empire.
A German historical term for Ukraine would be a mark – a term for the state’s borderland which existed from the time of the Frankish Kingdom/Empire of Carl the Great. The term is mostly used from the time of the Treaty (truce) of Andrussovo in 1667 between these two states. In other words, Ukraine and the Ukrainians as a natural objective-historical-cultural identity never existed as it was considered only as a geographic-political territory between two other natural-historical entities (Poland and Russia).
All (quasi)historiographical mentioning of this land and the people as Ukraine/Ukrainians referring to the period before the mid-17th century are quite scientifically incorrect but in the majority of cases politically inspired and colored with the purpose of presenting them as something crucially different from the historical process of ethnic genesis of the Russians [for instance: Alfredas Bumblauskas, Genutė Kirkienė, Feliksas Šabuldo (sudarytojai), Ukraina: Lietuvos epocha, 1320−1569, Vilnius: Mokslo ir enciklopedijų leidybos centras, 2010].
It was a Roman Catholic Vatican that was behind the process of creation of the “imagined community” of the “Ukrainian” national identity for the very political purpose of separating the people from this borderland territory from the Orthodox Russian Empire. Absolutely the same was done by Vatican’s client Austria-Hungary in regard to the national identity of the Bosnian-Herzegovinian population when this province was administered by Vienna-Budapest from 1878 to 1918 as it was the Austro-Hungarian government created totally artificial and very new ethnolinguistic identity – the “Bosnians”, just not to be the (Orthodox) Serbs (who were at that time a strong majority of the provincial population) [Лазо М. Костић, Наука утврђује народност Б-Х муслимана, Србиње−Нови Сад: Добрица књига, 2000.].
The creation of ethnolinguistically artificial Ukrainian national identity and later on a separate nationality was part of a wider confessional-political project by the Vatican in the Roman Catholic historical struggle against Eastern Orthodox Christianity (the eastern “schism”) and its Churches within the framework of Pope’s traditional proselytizing policy of reconversion of the “infidels”.
One of the most successful instruments of a soft-way reconversion used by the Vatican was to compel a part of the Orthodox population to sign with the Roman Catholic Church the Union Act recognizing in such a way a supreme power by the Pope and dogmatic filioque (“and from the Son” – the Holy Spirit proceeds and from the Father and the Son).
Therefore, the ex-Orthodox believers who now became the Uniate Brothers or the Greek Orthodox believers became in a great number later pure Roman Catholics but also changed their original (from the Orthodox time) ethnolinguistic identity. It is, for instance, very clear in the case of the Orthodox Serbs in the Zhumberak area of Croatia – from the Orthodox Serbs to the Greek Orthodox, later the Roman Catholics, and finally today the Croats. Something similar occurred in the case of Ukraine.
On October 9th, 1596 it was announced by Vatican a Brest Union with a part of the Orthodox population within the borders of the Roman Catholic Lithuanian-Polish Commonwealth (today Ukraine) [Arūnas Gumuliauskas, Lietuvos istorija: Įvykiai ir datos, Šiauliai: Šiaures Lietuva, 2009, 44; Didysis istorijos atlasas mokyklai: Nuo pasaulio ir Lietuvos priešistorės iki naujausiųjų laikų, Vilnius: Leidykla Briedis, (without year of publishing) 108.]. The crucial issue in this matter is that today Ukraina’s Uniates and the Roman Catholics are most anti-Russian and of the Ukrainian national feelings. Basically, both the Ukrainian and the Belarus present-day ethnolinguistic and national identities are historically founded on the anti-Orthodox policy of the Vatican within the territory of the ex-Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth that was in essence an anti-Russian one.
The Lithuanian historiography writing on the Church Union of Brest in 1596 clearly confirms that:
“… the Catholic Church more and more strongly penetrated the zone of the Orthodox Church, giving a new impetus to the idea, which had been cherished since the time of Jogaila and Vytautas and formulated in the principles of the Union of Florence in 1439, but never put into effect – the subordination of the GDL Orthodox Church to the Pope’s rule” [Zigmantas Kiaupa et al, The History of Lithuania Before 1795, Vilnius: Lithuanian Institute of History, 2000, 288].
In other words, the rulers of the Roman Catholic Grand Duchy of Lithuania (the GDL) from the very time of Lithuania’s baptizing in 1387−1413 by the Vatican had a plan to Catholicize all Orthodox believers of the GDL among whom the overwhelming majority were the Slavs. As a consequence, the relations with Moscow became very hostile as Russia accepted the role of the protector of the Orthodox believers and faith, and therefore the Church Union of Brest was seen as a criminal act by Rome and its client the Republic of Two Nations (Poland-Lithuania).
Today, it is absolutely clear that the most pro-western and anti-Russian part of Ukraine is exactly West Ukraine – the lands that were historically under the rule of the Roman Catholic ex-Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth and the former Habsburg Monarchy.
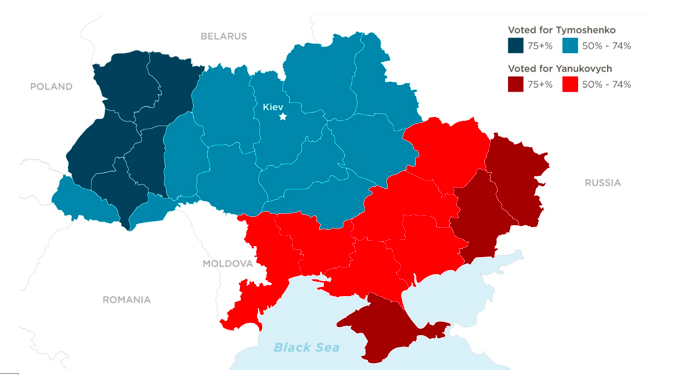
It is obvious, for instance, from the presidential voting results in 2010 that the pro-western regions voted for J. Tymoshenko while the pro-Russian regions did for V. Yanukovych. It is a reflection of the post-Soviet Ukrainian identity dilemma between “Europe” and “Eurasia” – a dilemma that is of common nature for all Central and East European nations which historically played the role of a buffer zone between the German Mittel Europa project and the Russian project of a pan-Slavonic unity and reciprocity.
The 2010 Presidential election voting results
In general, the western territories of present-day Ukraine are mainly populated by the Roman Catholics, the East Orthodox, and the Uniates. This part of Ukraine is mostly nationalistic and pro-western oriented. East Ukraine is in essence Russophone and subsequently “tends to look to closer relations with Russia” [John S. Dryzek, Leslie Templeman Holmes, Post-Communist Democratization: Political Discourses Across Thirteen Countries, Cambridge−New York: Cambridge University Press, 2002, 114].
*
Note to readers: Please click the share button above. Follow us on Instagram and Twitter and subscribe to our Telegram Channel. Feel free to repost and share widely Global Research articles.
Dr. Vladislav B. Sotirović is a former university professor in Vilnius, Lithuania. He is a Research Fellow at the Center for Geostrategic Studies. He is a regular contributor to Global Research.
Featured image is from Atlantic Council