NATO Preparing for Large-scale, High-intensity Armed Conflict with Russia?

All Global Research articles can be read in 51 languages by activating the “Translate Website” drop down menu on the top banner of our home page (Desktop version).
To receive Global Research’s Daily Newsletter (selected articles), click here.
Visit and follow us on Instagram at @crg_globalresearch.
***
We are at a Dangerous Crossroads in the History of Humanity.
Rick Rozoff provides us with a selection of excerpts from major Russian media sources pertaining to the Russia- US/NATO confrontation on Russia’s Western border with Ukraine.
The objective is to inform Western readers on how the official Russian media views and analyses this ongoing crisis which could lead the World into a World War III Scenario.
The excerpts include statements by Russia’s Defense Ministry
***
Emphasis added
1. Russian Information Agency Novosti.
Graphics supplied by Anti-Bellum
Defense Ministry: NATO is preparing for a large-scale armed conflict with Russia
“NATO is preparing for an armed conflict with Russia , Deputy Defense Minister Alexander Fomin said at a briefing for military attachés and representatives of foreign embassies accredited in Moscow.
“The military construction of the bloc has been completely redirected to prepare for a large-scale, high-intensity armed conflict with Russia,” the colonel-general said.
He explained that the North Atlantic Alliance in its documents, including the military strategy of 2019, directly calls our country the main source of “threats to coalition security.”
At the same time, Fomin noted, the Rome Declaration is still in force, which states that Russia and NATO do not consider each other as adversaries. The parties confirmed this at the 2010 summit in Lisbon. [At which Dmitry Medvedev became the first and to date only Russian or Soviet head of state to participate in a NATO summit – RR]
Targeted provocations by NATO near the Russian borders are highly likely to lead to an armed conflict, the Deputy Defense Minister emphasized. As an example, he cited the attempt of the British destroyer Defender in June of this year to penetrate the territorial waters of Russia off the coast of Crimea. At the same time, the actions of the British Navy ship were provided by the American strategic reconnaissance aircraft RC-135.
As Fomin pointed out, the intensity of such flights in the Black Sea region increased by more than 60 percent compared to 2020, the number of sorties increased from 436 to 710. Strategic bombers B-IB and B-52H of the US Air Force flew 92 times against 78 in 2020 in the airspace of the Black Sea region with access to the conditional line of using weapons. To the west of Crimea, the planes flew up to the Russian borders at a distance of 15 kilometers.
“In total, this year, the command of the NATO Joint Armed Forces conducted 15 exercises in the Black Sea. In 2020, there were eight,” the Deputy Defense Minister continued.
The presence of ships and auxiliary vessels from non-regional NATO states “has become virtually permanent.”
“From January to December of this year, 30 calls of NATO ships were made, in 2020 there were 23 of them. The total duration of stay was more than 400 days, in 2020 – 359,” Fomin said.
Activity in the Baltic region
In the Baltic zone, aircraft of NATO countries made more than 1,200 sorties, and more than 50 warships went out for naval reconnaissance. More than 20 exercises were held in the region in 2021.
“At the same time, neutral states and our closest neighbors: Finland and Sweden are actively involved in coalition activities ,” the colonel-general noted.
He also stressed that after the US withdrew from the Treaty on the Elimination of Intermediate-Range and Shorter-Range Missiles, NATO actually ignored Vladimir Putin ‘s initiative to impose a moratorium on the deployment of new intermediate and shorter-range missiles in Europe and the possibility of developing reciprocal measures to remove existing fears.
“Every year, the NATO bloc conducts 30 major exercises, during which scenarios for conducting military operations against Russia are being worked out. Within the framework of combat training events, special attention is paid to the creation of strike groups near the borders of our country. In particular, a series of Defender exercises were held in May-June of this year. Europe-2021 with the transfer from the United States of America and Western Europe to the “eastern flank” of reinforcement troops of up to 40 thousand people,” Fomin said.”
***
At the same time, a contingent of about 13 thousand troops from the non-regional states of the bloc is constantly present in Eastern Europe. It has about 200 tanks, 400 armored vehicles, 50 guns and three dozen aircraft and helicopters.
====
2. From Sputnik News
Russian Defence Ministry: NATO Preparing for Large-scale High-intensity Conflict With Moscow
Moscow has expressed concerns about the concentration of Western alliance missile systems, troops, warships and aircraft near Russia’s borders, and NATO’s decades’ long eastward expansion. This month, the Russian Foreign Ministry formally signalled that it considers Ukraine to be a ‘red line’ for Moscow which NATO is strongly advised not to cross.
NATO is preparing for a large-scale armed conflict with Russia, in contravention of the Rome Declaration of 2002, Russian Deputy Defence Minister Alexander Fomin has said.
***
From Drang nach Osten “Push Eastwards”
[Russia’s] deputy defence minister warned that NATO’s efforts to expand and strengthen its military infrastructure on its eastern flank have had a negative impact on the security architecture of the entire European continent, but are only one of multiple actions taken by the alliance over the decades to do so.
“In 1999, a military operation which was not approved by the United Nations was carried out in Yugoslavia. The bombing of Belgrade killed innocent civilians, and the country’s economy was disrupted. The disintegration of Yugoslavia led to a new round expansion of the bloc and the incorporation of Albania, Croatia and Montenegro, and after that Northern Macedonia,” Fomin said.
At the same time, he noted, the ‘Western partners’ continued to assure Moscow “of the absence of aggressive designs against Russia,” and that Russia believed these assurances, notwithstanding the freezing of interaction with NATO in 1999 in connection with the Yugoslav crisis.
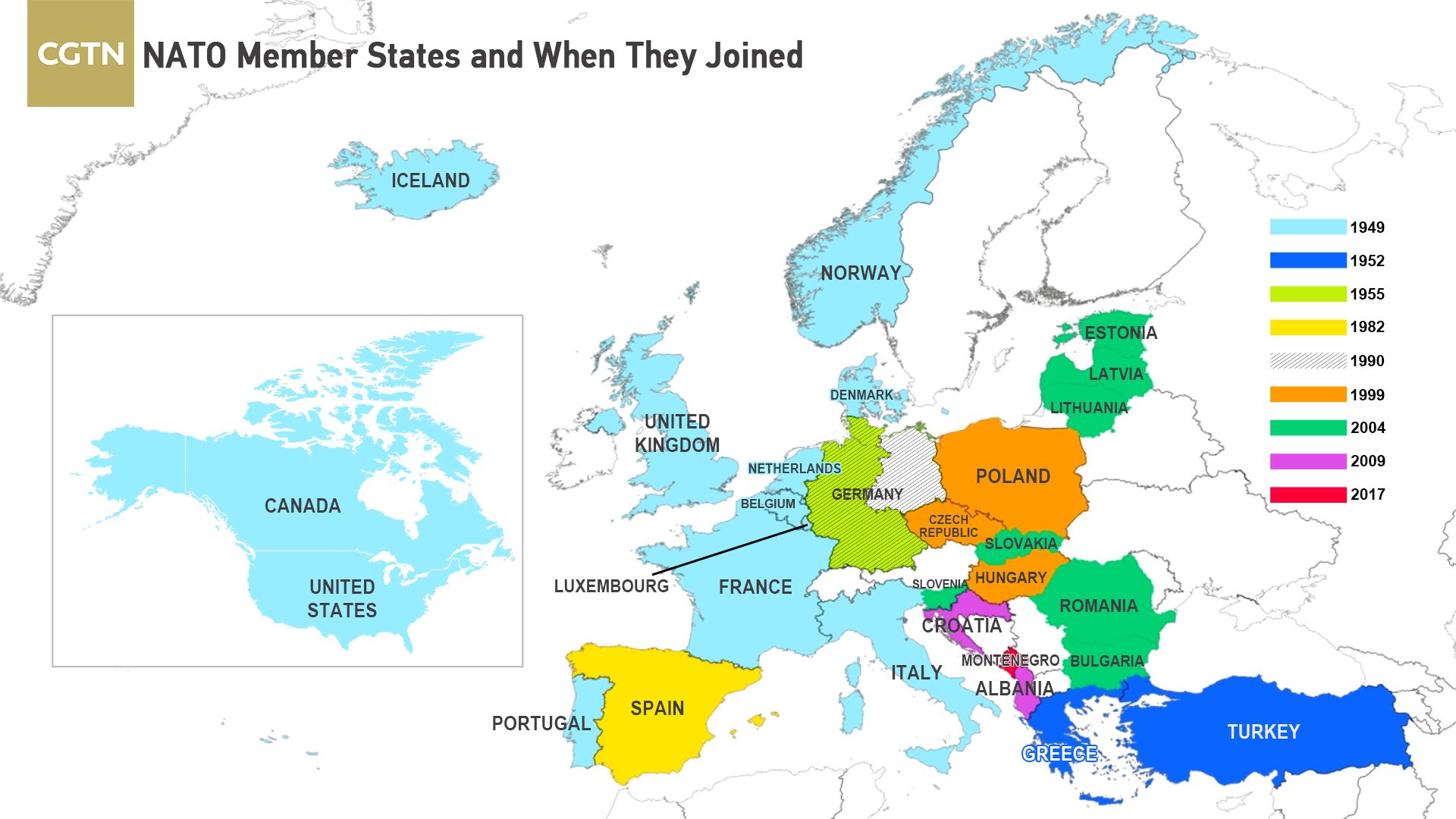
Fomin recalled that the most significant expansion of NATO eastward took place in 2004, when the Baltic states of Latvia, Lithuania and Estonia, as well as Bulgaria, Romania, Slovakia and Slovenia joined the bloc.
This and other waves of expansion significantly increasing the alliance’s military potential on its eastern flank, he said, pointing out that NATO’s borders have moved over 1,000 km eastward, providing it with opportunities to use non-strategic weapons to strike targets inside Russia.
“For example, the minimum flight time from air bases in Estonia to St. Petersburg has been reduced to several minutes. Most of Kaliningrad region is within striking range of artillery systems alone….A significant number of pieces of infrastructure have been transferred to NATO’s disposal, expanding the possibility for the deployment and transfer of troops,” Fomin said.
.
The officer added that the bloc’s arsenal was beefed up considerably by weapons, vehicles and personnel of the former Warsaw Pact members, plus new ports in the Baltic and Black Seas, and an expansion of NATO’s naval forces.
From TASS
Russian Defense Ministry says NATO aims to deter, not engage with Russia
NATO has focused on the military deterrence of Russia while it used to prefer engaging in joint projects, said Russian Deputy Defense Minister Alexander Fomin.
“The current deplorable state of relations between Russia and NATO can be explained by the fact that the alliance has often resorted to using hybrid methods to contain Russia, combining dialogue with a build-up of military preparations,” Fomin said on Monday….
He said that the deterioration of relations between Russia and NATO began earlier than 2014.
“After the end of the Cold War, the Russian Federation has repeatedly made attempts to find new forms of engagement with NATO, to create a stable, equal system of European security for all,” Fomin said. “It would be wrong to believe that the deterioration of Russia-NATO relations began in 2014.”
“The declared goals of equal cooperation by the alliance were not fulfilled much earlier, in fact, immediately after the collapse of the Warsaw Pact,” he went on to say. “At the same time, Russia was then unprecedentedly open to constructive partnership with the West and carried out a voluntary demilitarization of the country on its western borders.”
Russia also withdrew its troops from the Warsaw Pact countries, the deputy minister said.