Treasury Now Has Color-Coded Financial Terror Alerts

Remember when the Department of Homeland Security was issuing those color-coded terrorist alerts? Well, they don’t do that anymore. They’re back to using plain ole black-and-white words to describe threats.
Apparently, however, the U.S. Treasury’s Office of Financial Research (OFR) thought it was such a cool idea that they’ve started color-coding threats to our financial security from the denizens on Wall Street: the gang that brought our country to its knees in 2008 while the most expensive military in the world was hunting down robed cave-dwellers in the Middle East.
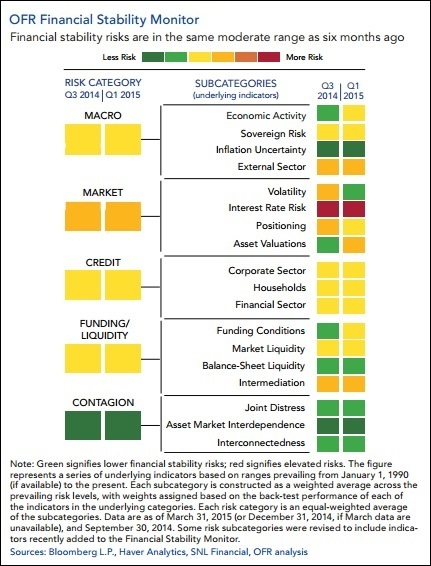
OFR’s color-threat alert is called the Financial Stability Monitor. The monitor is based on approximately 60 indicators and organized as a heat map: The closer an indicator is to the red end, the more elevated the risks; the closer an indicator is to the green end of the spectrum, the lower the risks. The Monitor, released yesterday, says that “financial stability risks remain moderate.”
Unfortunately, when we studied the accompanying chart, we found that it’s based on first quarter data, meaning it’s almost three months old. (Imagine Homeland Security issuing a terrorist alert, then telling you it might not be all that reliable because it’s based on stale intelligence.)
Nonetheless, there’s some very interesting takeaways from the Monitor. First, even though the OFR has characterized the financial stability threat as “moderate,” a close reading of the report suggests a heightened threat. These are some key points from the report:
- Financial and economic risks have further decoupled, with financial risk-taking occurring against the backdrop of a tepid growth recovery.
- Global monetary policies and economic growth continue to diverge. Central banks in some advanced economies, led by the European Central Bank and the Bank of Japan, are conducting highly expansionary monetary policies, while in the United States, the Federal Reserve is closer to embarking on a tightening cycle.
- Foreign risks have increased, including intensified government financing risks in Greece and weakening economic fundamentals in key emerging markets.